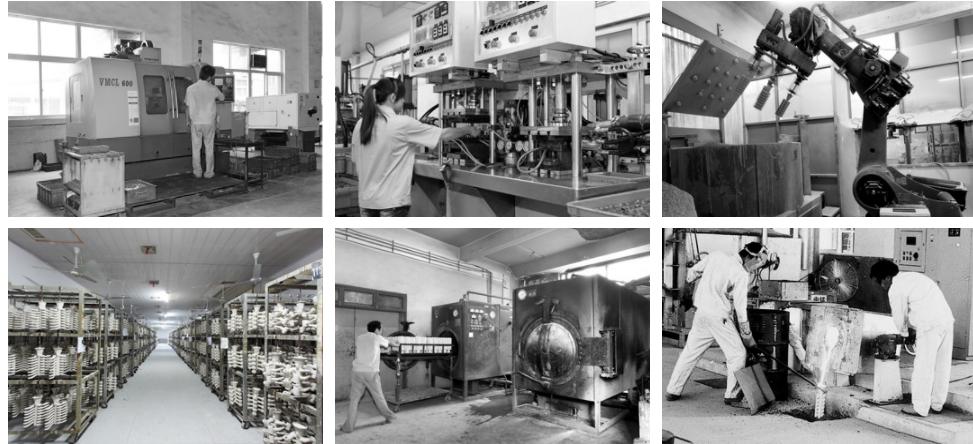
Die casting die is a tool for casting metal parts, a tool for completing the die casting process on a special die casting die forging machine. The basic process of die casting is that the liquid metal is first cast at low or high speed and filled into the cavity of the die. The die has an active cavity surface, which is forged under pressure along with the cooling process of the liquid metal, not only to eliminate the shrinkage cavity and porosity defects of the blank, but also to make the internal structure of the blank reach the forged broken grain. The comprehensive mechanical properties of the blank are remarkably improved.
Chinese name
Die casting mould
Foreign names
Die casting mould
This mass
A method of liquid die forging
The technological process
The liquid metal is first cast at low or high speed
Three main factors
Die casting material, die casting machine,
Die casting material, die casting machine and die are the three main elements of die casting production. The so-called die casting process is to use these three elements organically and comprehensively, so that it can produce qualified castings with good appearance, internal quality, size conforming to the requirements of the drawing or the agreement steadily and efficiently, or even high quality castings.
The alloy used in die casting is mainly non-ferrous alloy, as for the ferrous metal (steel, iron, etc.) due to the problems of mold materials, less use. In the non-ferrous alloy die casting, aluminum alloy is widely used, followed by zinc alloy. Here is a brief introduction to die – casting nonferrous metals.
(1) the classification of die casting non-ferrous alloy is blocked mixed contraction free shrinkage lead alloy – 0.2-0.3-0.4-0.4% and 0.5% 0.3% low melting point alloy tin alloy zinc alloy — — — — — — — – 0.3-0.6-0.4-0.6% 0.4% and 0.8% Al-si series 0.7 0.5-0.3-0.5% – 0.7% – 0.9% of die casting non-ferrous alloy aluminum alloy aluminum bronze series aluminum magnesium – 0.5-0.7-0.9-0.9% and 1.1% 0.7% high melting point alloy aluminum zinc series magnesium alloys — — — — — — — — — – 0.5-0.7-0.9% 0.7% 0.9 1.1% of copper alloy

(2) The recommended casting temperature for all kinds of die casting alloys: the average wall thickness of castings of alloy types is less than or equal to 3mm, the average wall thickness of castings > 3mm simple structure complex structure simple structure complex structure
Aluminum alloy aluminum silicon series 610-650℃ 640-680℃ 600-620℃ 610-650℃
Aluminum copper system 630-660℃ 660-700℃ 600-640℃ 630-660℃
Aluminum magnesium series 640-680℃ 660-700℃ 640-670℃ 650-690℃
Aluminum and zinc series 590-620℃ 620-660℃ 580-620℃ 600-650℃
Zinc alloy 420-440℃ 430-450℃ 400-420℃ 420-440℃
Magnesium alloy 640-680℃ 660-700℃ 640-670℃ 650-690℃
Copper alloy common brass 910-930℃ 940-980℃ 900-930℃ 900-950℃
Silicon brass 900-920℃ 930-970℃ 910-940℃ 910-940℃
* Note: ① The casting temperature is generally measured by the temperature of the liquid metal in the holding furnace.
(2) The casting temperature of zinc alloy should not exceed 450℃ to avoid coarse grains.
The design process
Edit the voice
1, according to the type of materials used in the product, product shape and precision and other indicators of the product process analysis, determine the process.
2. Determine the placement of products in the mold cavity, analyze and design the parting surface, drainage system and pouring system.
3. Design the assembling and fixing modes of the core of each activity.
4. Design of core-pulling distance and force.
5. Design of ejection mechanism.
6. Determine the die casting machine, and design the die frame and cooling system.
7. Check the relative dimensions of molds and die casting machines, and draw the process drawings of molds and various parts.
8. Design completion [1].

Frequently Asked Questions
The control of the surface temperature of die casting die is very important for the production of high quality die castings. Uneven or inappropriate die casting temperature can also lead to unstable casting size and deformation of the casting during the production process, resulting in defects such as thermal pressure, sticking mold, surface sag, internal shrinkage cavity and hot bubble. When the mold temperature is different, the variables in the production cycle, such as filling time, cooling time and spraying time, will be affected to different degrees.
1). Cold lines:
Reason: the temperature of the front end of melting soup is too low, and there are traces of overlapping
Improvement methods:
1. Check if the wall thickness is too thin (design or manufacture), thinner areas should be filled directly
2. Check that the shape is not easy to fill; Too far away, closed areas (e.g., fin, bulge), blocked areas, too small fillet, etc., are not easy to fill. And watch for ribs or cold spots
3. Shorten the filling time, shorten the filling time method
4. Change filling mode
5. Methods of increasing mold temperature
6. Raise the temperature of the soup
7. Check alloy composition
8. Expanding the escape route may help
9. A vacuuming device may be useful
2). Crack:
The reason:
1. Shrinkage stress
2. Cracked under pressure on ejection or entire edge
Improvement methods:
1. More rounded corners
2. Check whether there is a hot spot
3. Pressurization time change (cold chamber machine)
4. Increase or shorten mold closing time
5. Increase the drawing Angle
6. Add the ejection pin
7. Check whether the mold is misplaced or deformed
8. Check alloy composition
(3). Porosity:
The reason:
1. Air is mixed in the soup
2. Gas source: melting, in the pipe, in the mold, release agent
Improvement methods:
1. Slow down
2. Check if the runner turns smoothly and the cross-sectional area is decreasing
3. Check to see if the area of the escape duct is large enough, if it is obstructed, and if it is located at the last filling place
4. Check whether the release agent is sprayed too much and the mold temperature is too low
5. Use the vacuum
4). Cavitation erosion:
Cause: Due to the sudden decrease of pressure, the gas in the melting soup suddenly expanded, impacting the mold and causing mold damage
Improvement methods:
The cross-sectional area of the flow channel should not change sharply
5). Shrinkage cavity:
Reason: When a metal solidifies from a liquid state to a solid state, the space occupied by the metal becomes smaller. If there is no metal supplement, shrinkage cavity will form, usually at a slower solidification place
Improvement methods:
1. Increase the pressure
2. Change the mold temperature. Local cooling, spray type agent, reduce mold temperature. Sometimes just change the location of the shrinkage hole, rather than the shrinkage hole
6). Peeling:
The reason:
1. Poor filling mode, resulting in melting soup overlap
2. Mold deformation, resulting in melting soup overlap
3. Inclusion oxide layer
Improvement methods:
1. Switch to high speed early
2. Shorten filling time
3. Change filling mode, gate position, gate speed
4. Check mold strength is sufficient
5. Check whether the pin and die devices are in good condition
(6. Check for inclusion of oxide layer
7). Bellows:
Reason: The first layer of melting soup cools rapidly on the surface, while the second layer of melting soup flows through and fails to melt the first layer, but it has enough fusion to cause different tissues
Improvement methods:
1. Improved filling mode
2. Shorten filling time
8). Holes caused by poor flow:
Cause: The soup flows too slowly, or is too cold, or the filling pattern is poor, so there are holes in the solidified metal joints
Improvement methods:
1. The same method of improving cold stripe
2. Check whether the temperature of the melting soup is stable
3. Check whether the temperature charge of the mold is stable
9). Hole in parting surface:
Cause: It could be shrinkage or blowhole
Improvement methods:
1. In case of shrinkage, reduce the thickness of gate or overflow inlet
2. Cooling gate
3. If there are air holes, pay attention to exhaust or air trapping
10). Flash:
The reason:
1. Clamping force is insufficient
2. Bad mold closing
3. Insufficient die strength
4. The soup is too hot
11). Shrinkage in:
Cause: Shrinkage occurs below the pressure surface
Improvement methods:
1. Methods to improve shrinkage cavity
2. Local cooling
3. Heat the other side
12). Carbon deposition:
Cause: release agent or other impurities accumulated on the mold.
Improvement methods:
1. Reduce the amount of release agent spray
2. Higher mold temperatures
3. Select suitable release agent
4. Use soft water to dilute the release agent
13). Bubble: